eSIM Security Protocols: What You Need to Know
https://www.zimconnections.com/esim-security-protocols-what-you-need-to-know/
 SHARE
SHARE
eSIMs are changing how devices connect to mobile networks by replacing physical SIM cards with embedded chips. They allow you to download and switch operator profiles digitally while offering strong security protections. Here’s what you should know:
- What is an eSIM? It’s a chip built into your device that replaces traditional SIM cards. You can store multiple profiles but only use one at a time.
- Security Focus: eSIMs use encryption, IMSI masking (hiding your subscriber identity), and secure communication protocols like TLS to protect your data.
- Key Features: Remote profile management, authentication via QR codes or activation codes, and protection against SIM theft or cloning.
- Benefits for Travellers: Easily switch to local data plans without needing physical cards, reducing roaming costs by up to 90%.
- Best Practices: Use trusted providers, keep devices updated, and secure your phone with strong passwords and biometric locks.
eSIMs offer a safer, more convenient way to stay connected while prioritising privacy and reducing the risks tied to physical SIM cards.
How eSIM Security Protocols Work
Encryption and Data Protection
eSIM technology relies on encryption to keep your data secure and inaccessible to unauthorised parties. One key feature is IMSI masking, which conceals the International Mobile Subscriber Identity, making it harder for fake cell towers to track users. Additionally, any geolocation data transmitted is encrypted to ensure your physical location remains private unless authorised access is granted.
| Security Mechanism | Technical Function | Security Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| IMSI Masking | Hides or replaces the unique subscriber identity | Prevents tracking and interception by IMSI catchers |
| Geolocation Encryption | Encrypts GPS and location-based data packets | Ensures the user cannot be located or tracked without authorisation |
| Data Encryption | Protects all transmitted data during communication | Prevents data from being manipulated, shared, or sold |
This multi-layered encryption also plays a vital role in the authentication process when installing eSIM profiles.
Authentication Processes
eSIM profiles are installed securely through authentication methods like scanning a QR code or manually entering an SM-DP+ address with an activation code. This ensures the profile is sent only to the intended device, identified by its unique 32-digit EID. Some providers enhance security further by requiring a 4-digit confirmation code, which is either sent via SMS or provided at the time of purchase.
In some cases, carriers use secure push notifications to directly trigger the download of the eSIM profile to your device.
Remote Profile Management Security
Once authentication is complete, remote profile management ensures the secure exchange of data. The GSMA’s remote SIM provisioning (RSP) protocol enforces the use of TLS encryption to protect communications between the Subscription Manager (SM-DP+) and your device’s eUICC chip. This encryption ensures the data cannot be intercepted or tampered with during profile downloads.
A key security feature is signature-chaining, which cryptographically links each provisioning message. This mechanism ensures that any attempt to substitute or replay messages will fail verification. The GSMA confirms, “The signature-chaining mechanism prevents the adversary from replacing partial messages and/or signatures”.
In August 2024, researchers at Aalto University in Finland conducted a security analysis of the Consumer Remote SIM Provisioning Protocol (SGP.22 v2.3). Their findings, presented at Black Hat Europe in December 2024, highlighted the effectiveness of signature-chaining and TLS in mitigating risks like message replacement and replay attacks. The GSMA’s assessment supported these conclusions.
To further bolster security, all entities in the eSIM ecosystem are required to obtain PKI certificates from the GSMA. These certificates ensure that only authorised servers can interact with your device. Additionally, the eUICC chip is designed to meet EAL4+ security certification under the GSMA eUICC Protection Profile (SGP.25), offering strong resistance against advanced attacks.
Vulnerabilities in the eSIM download protocol
Benefits of eSIM Security Protocols
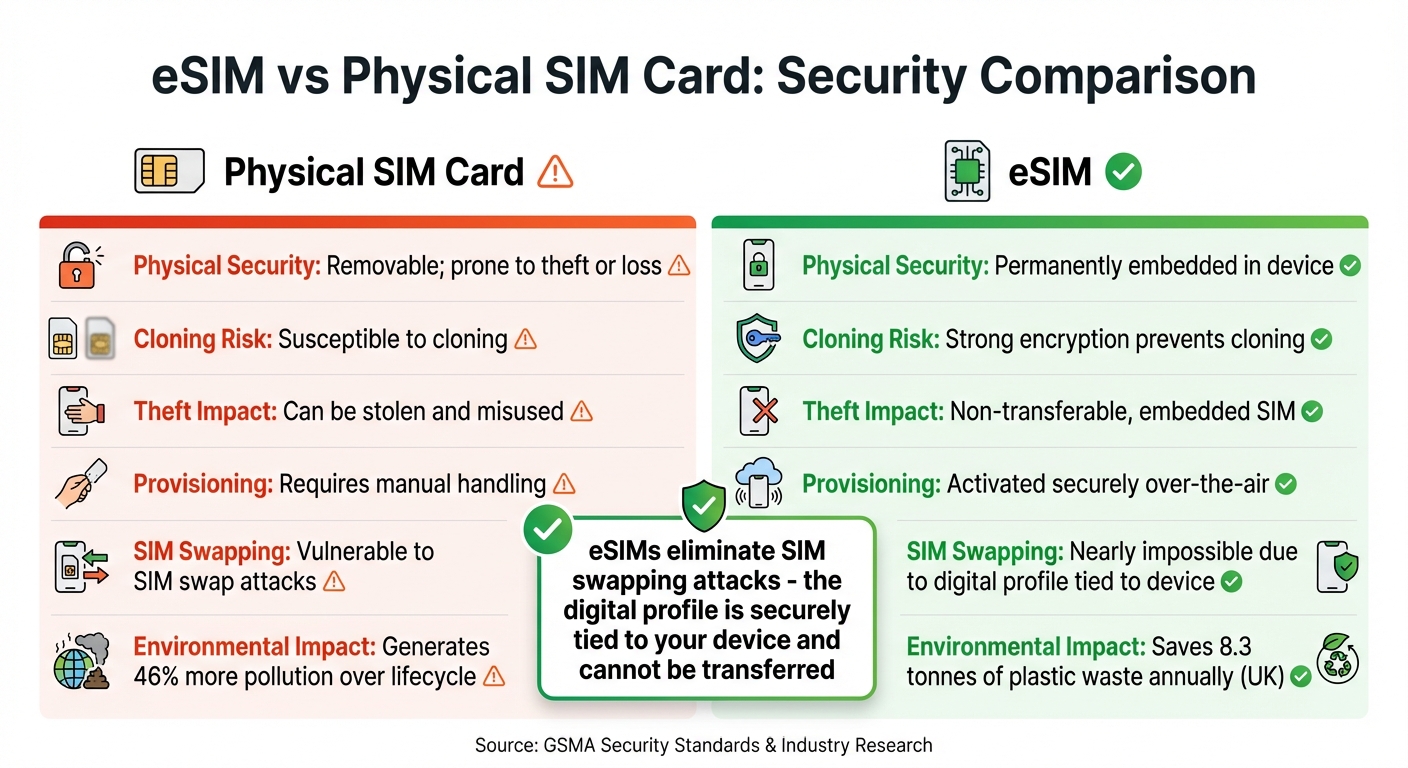
eSIM vs Physical SIM Card Security Comparison
Better Privacy and Data Protection
eSIM technology brings a new level of privacy and data security compared to traditional SIM cards. At its core lies the Secure Element, a hardware-based vault embedded in your device. This permanent feature meets or even surpasses the security standards of removable SIMs, offering strong protection against advanced hacking attempts and unauthorised access.
Another key advantage is the strict oversight of the eSIM lifecycle. The GSMA’s Security Accreditation Schemes, covering both production sites (SAS-UP) and operational processes (SAS-SM), ensure that every environment handling eSIM data adheres to rigorous security protocols.
"The stringent security requirements outlined in the eUICC Protection Profile ensure that the eUICC software components are able to protect and safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorised access." – GSMA
For those who value privacy, some eSIM solutions allow users to bypass traditional SIM registration or the need to provide personal information, enhancing anonymity. All data is securely encrypted, removing the risks associated with handling a physical SIM card.
These advanced privacy features not only safeguard your sensitive information but also contribute to a smoother, safer experience when staying connected abroad.
Convenience for International Travellers
eSIMs combine security with convenience, especially for international travellers. By enabling users to purchase and activate data plans online before leaving home, eSIMs reduce the need to rely on public Wi-Fi networks or unfamiliar vendors at airports.
Travellers can also enjoy significant savings – up to 90% – on roaming fees compared to traditional international plans. Businesses with global teams can benefit too. For example, ZIM Connections provides prepaid eSIM voice and data plans with 5G/4G coverage in over 200 destinations, ensuring secure and seamless connectivity.
Another advantage is the ability to use dual-SIM functionality. You can keep your primary physical SIM for essential calls and texts while using an eSIM for affordable local data. This setup not only saves money but also keeps your primary number private, reducing the risk of cybersecurity threats while travelling.
The security features of eSIMs align perfectly with their digital convenience, making them an ideal choice for frequent travellers.
Reduced Risk of SIM Card Theft or Loss
eSIM technology eliminates the physical vulnerabilities associated with traditional SIM cards. Since the eUICC chip is permanently embedded in your device, it cannot be removed or stolen. This design greatly reduces risks like theft or unauthorised use.
| Security Aspect | Physical SIM Card | eSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Security | Removable; prone to theft or loss | Permanently embedded |
| Cloning Risk | Susceptible to cloning | Strong encryption prevents cloning |
| Theft Impact | Can be stolen and misused | Non-transferable, embedded SIM |
| Provisioning | Requires manual handling | Activated securely over-the-air |
Traditional SIM swapping attacks – where fraudsters trick mobile operators into transferring your number to another SIM – are nearly impossible with eSIMs. The digital profile is securely tied to your device and cannot be moved to another one. This eliminates the hassle of carrying or swapping physical SIM cards, particularly during international travel.
Additionally, eSIMs contribute to environmental sustainability. In the UK alone, they save an estimated 8.3 tonnes of plastic waste annually and generate 46% less pollution over their lifecycle compared to traditional SIM cards.
"eSIMs mark a turning point in mobile security. With its built-in encryption, remote provisioning, and immunity to physical tampering, eSIMs offer a safer, more resilient alternative." – Voye Global Team
sbb-itb-273ea09
Best Practices for Safe eSIM Usage
Use Trusted Providers Like ZIM Connections
Opting for a well-established provider like ZIM Connections ensures that your eSIM profiles are delivered through encrypted channels, using mutual authentication between your device and secure servers. This significantly reduces the risk of falling victim to eSIM scams, where fraudsters might use fake QR codes to install malware or steal your data.
Top-tier providers follow GSMA standards, which means your digital profiles are stored securely within tamper-resistant hardware on your device. They also provide secure payment options and responsive customer support to quickly address issues like lost devices or suspicious activity.
"GSMA certification is a rigorous process that confirms an eSIM solution complies with stringent security, functionality and interoperability standards." – CSG Blog
Always purchase eSIMs directly from official sources, such as the provider’s app or website. Avoid third-party sellers on platforms like Telegram or WhatsApp, and double-check the legitimacy of the provider’s website. When activating your eSIM, connect to a trusted home or mobile network to ensure a secure setup. Taking these steps lays the groundwork for protecting your device and its software.
Keep Your Device Updated
Keeping your device’s software up to date is a key part of eSIM security. Regular updates not only deliver the latest security patches but also ensure your device remains compatible with GSMA-standard protocols. Modern devices come with hardware-based security features, such as Secure Elements or Trusted Execution Environments, which work in tandem with updated software to protect your eSIM profiles.
To minimise risks from outdated software, enable automatic updates on your device. While eSIM technology already uses advanced encryption methods – like AES‑256 for stored data and TLS 1.3 for data in transit – consistent updates further strengthen security for both your eSIM and the device as a whole.
Secure Your Device with Strong Passwords
Even with robust eSIM security measures in place, your device itself is the gateway to your eSIM and must be protected. Many risks, such as account takeovers or malicious QR codes, stem from weak personal security practices.
Use strong passcodes and biometric locks, like Face ID or fingerprint recognition, to secure your device. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on key accounts, including your carrier account, email, and Apple or Google IDs, to block unauthorised access. Additionally, set a unique security PIN for your mobile carrier account to guard against SIM swap attacks.
Activate device location tracking so you can remotely lock or wipe your device if it’s lost or stolen. Treat your eSIM activation QR code as you would a password – scan it in private and never share screenshots or display it publicly. For tasks involving sensitive information, such as online banking or work emails, use your mobile data rather than public Wi-Fi. Mobile networks, especially 4G and 5G, offer stronger encryption and are much harder to compromise.
| Network Type | Encryption Standard | Security Level |
|---|---|---|
| 5G | 256‑bit encryption | Highest |
| 4G/LTE | 128‑bit encryption | High |
| 3G | 64‑bit encryption | Medium |
| 2G | Weak encryption | Low |
Be vigilant for signs of security issues, such as unexpected network changes, unexplained data usage spikes, or warnings about security certificates. These could indicate network interference. Once you’re back from a trip, delete any unused travel eSIM profiles to keep your device secure and organised.
Conclusion
Summing up the insights shared earlier, here’s a concise look at how eSIM technology has transformed mobile security and connectivity.
eSIMs deliver security measures comparable to traditional SIM cards. The embedded Secure Element in devices, combined with TLS protocols, creates a strong barrier against network-based threats. This approach ensures that sensitive data stays encrypted during profile downloads and activations, with signature-chaining mechanisms in place to prevent tampering.
For frequent travellers, eSIMs bring both practicality and enhanced security. The ability to switch operator profiles remotely eliminates the need to handle physical SIM cards. As mentioned earlier, GSMA enforces strict standards for certified providers, with the eUICC Protection Profile aiming for EAL4+ certification to counter sophisticated attacks. These certifications are regularly updated to keep pace with emerging security threats.
In the UK, eSIM adoption has grown rapidly, increasing by 287% between early 2023 and March 2024, with 14.3 million active eSIMs recorded. By 2025, nearly all mobile carriers – 98% – are expected to support eSIM plans, showing strong industry confidence in this technology.
Key Takeaways
Understanding eSIM security protocols can help you make smarter decisions about mobile connectivity. With built-in encryption, eSIMs offer robust protection without requiring technical knowledge from users. Unlike physical SIM cards, eSIMs are embedded in devices, reducing risks like SIM swapping and port-out scams.
To enhance your eSIM security, consider these best practices:
- Opt for GSMA-certified providers, such as ZIM Connections, which operate in trusted ecosystems.
- Keep your device software updated with the latest security patches.
- Use strong passwords and biometric locks for device access.
- Always erase eSIM data before selling or disposing of your device to avoid identity theft.
When travelling, you can take advantage of dual SIM features by keeping your primary number active while using a local eSIM for affordable data.
"The presence of these security measures evidence that the GSMA eSIM specifications have been designed with security by design in mind to protect the security and resilience of the endpoints and the communication between them." – GSMA
The rise of eSIM technology represents a significant step forward in securing mobile connections. By adopting informed practices, you can enjoy seamless global connectivity while safeguarding your data and privacy.
FAQs
How does eSIM technology make your device more secure than traditional SIM cards?
eSIM technology offers a higher level of security by embedding the SIM directly into your device, removing the need for a physical card. This eliminates risks like tampering or theft. Instead of relying on traditional SIM cards, eSIMs use remotely-provisioned profiles that are securely transferred through TLS (Transport Layer Security) connections, ensuring your sensitive data stays safe during activation and updates.
What’s more, eSIMs come with stringent certification processes to block threats like SIM-swapping and unauthorised access. This built-in protection often surpasses the security of removable SIM cards, making eSIMs a more secure option for staying connected, whether you’re at home or travelling abroad.
How can I keep my eSIM secure while travelling?
To keep your eSIM secure while travelling, make sure your device’s operating system and eSIM software are always updated. Protect your phone with a strong lock screen, like a PIN or biometric authentication, and activate a SIM PIN for an extra layer of security. When downloading eSIM profiles, stick to trusted, GSMA-certified providers.
Take time to regularly check your eSIM profiles and remove any that you no longer need. Stay cautious with public Wi-Fi – avoid unsecured networks, and if you must connect, use a VPN to safeguard your data. Additionally, enable features such as remote wipe or find my device to protect your personal information if your phone gets lost or stolen.
Are eSIMs fully protected against SIM-swapping and similar attacks?
While eSIMs rely on remote-provisioning protocols that are designed to match the security of physical SIM cards, they aren’t entirely immune to risks like SIM-swapping or similar attacks. Weaknesses could still emerge if systems managing provisioning or security protocols, such as TLS, are compromised.
That being said, eSIMs do provide some notable security benefits. For instance, they minimise the chances of physical theft or tampering. To keep your device and data safer, it’s a good idea to stick to best practices: enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and use strong, unique passwords to secure your device.